Module tf.browser.ner.ner
API for rule-based entity marking.
This module contains the top-level methods for applying annotation rules to a corpus.
To see how this fits among all the modules of this package, see
tf.browser.ner.annotate .
Programmatic annotation done in a Jupyter Notebook
If you have a spreadsheet with named entities, and for each entity a list of surface forms, then this module takes care to read that spreadsheet, translate it to YAML, and then use the YAML as instructions to add entity annotations to the corpus.
See this example notebook.
Here are more details.
Starting up
Load the relevant Python modules:
from tf.app import use
Load your corpus. There are two ways:
-
Work with a local GitHub clone of the corpus in
~/HuygensING/suriano:A = use("HuygensING/suriano:clone", checkout="clone") -
Or let TF auto-download the latest version and work with that:
A = use("HuygensING/suriano")
Load the Ner module:
NE = A.makeNer()
The tool expects some input data to be present: configuration and spreadsheets with
instructions. They can be found in the ner directory.
If you work with a local GitHub clone, that data resides in
~/github/HuygensING/suriano
and if you work with an auto-downloaded copy of the data, it is in
~/text-fabric-data/github/HuygensING/suriano.
The output data of the tool ends up in the _temp directory, which ends up next
to the ner directory.
The entity spreadsheets
Here is an example:
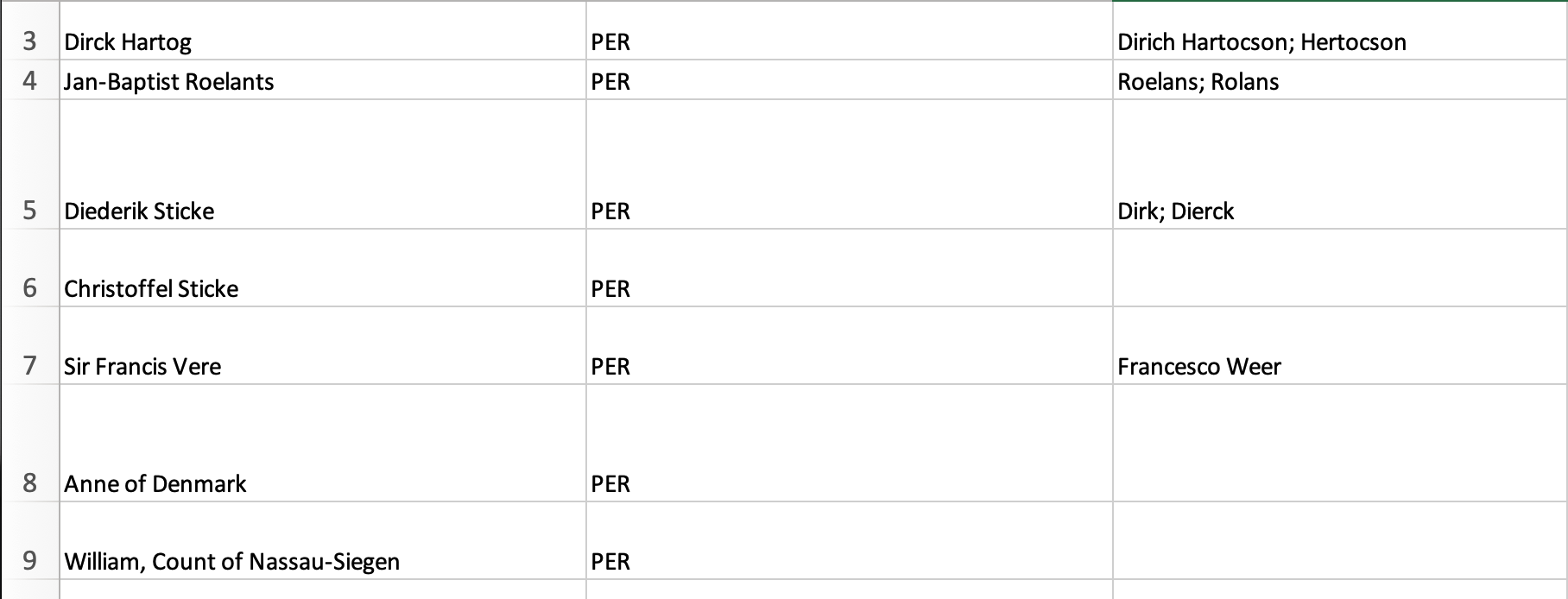
In our example, the name of the spreadsheet containing this information is
people.xlsx and it can be found as ner/sheets/people.xlsx
The spreadsheet will be read as follows:
- the first two rows will be skipped
- after that, each row is taken to describe exactly one entity
- the first column has the full and unique name for that entity
- the second column contains the kind of the entity (you may choose your keywords freely for this)
- the third column contains a number of surface forms for this entity,
separated by
; - when the surface forms are peeled out, leading and trailing white-space will be stripped
- all other columns will be ignored for the moment; in later versions we may use the information in those columns to fill in extra data about the entities; but probably that information will not end up in TF features.
During translation from XLSX to YAML the following happens:
- An identifier is distilled from the name of the entity;
- Missing kind fields are filled with the default kind.
These steps need some configuration information from the ner/config.yaml file.
Translation is done by
NE.readInstructions("people")
The resulting YAML ends up next to the spreadsheet, and it looks like this:
christoffel.sticke:
kind: PER
name: Christoffel Sticke
occSpecs: []
diederik.sticke:
kind: PER
name: Diederik Sticke
occSpecs:
- Dierck
- Dirk
dirck.hartog:
kind: PER
name: Dirck Hartog
occSpecs:
- Dirich Hartocson
- Hertocson
jan.baptist.roelants:
kind: PER
name: Jan-Baptist Roelants
occSpecs:
- Roelans
- Rolans
Inventory
A first step is to find out how many occurrences we find in the corpus for these surface forms:
NE.makeInventory()
NE.showInventory()
and the output looks like this
...
cornelis.adriaensz PER Pach 7 x Cornelis Adriaensz. Pack
david.marlot PER Morlot 1 x David de Marlot
erick.dimmer PER Dimer 11 x Erick Dimmer
erycius.puteanus PER Potiano 2 x Erycius Puteanus
francesco.giustiniani PER Giustiniano 11 x Francesco Giustiniani
francois.doubleth PER Doublet 2 x François Doubleth
...
Total 150
Entities that are in the spreadsheet, but not in the corpus are skipped.
Marking up
In order to create annotations for these entities, we have to switch to an
annotation set. Let's start a new set and give it the name power.
NE.setSet("power")
If it turns out that power has already annotations, and you want to clear them, say
NE.resetSet("power")
Now we are ready for the big thing: creating the annotations:
NE.markEntities()
It outputs this message:
Already present: 0 x
Added: 150 x
Inspection
We now revert to lower-level methods from the tf.browser.ner.annotate class to
inspect some of the results.
results = NE.filterContent(bFind="pach", bFindC=False, anyEnt=True, showStats=None)
Here we filtered the chunks (paragraphs) to those that contain the string pach,
in a case-insensitive way, and that contain at least one entity.
There 6 of them, and we can show them:
NE.showContent(results)

The resulting entities are in _temp/power/entities.tsv and look like this:
erick.dimmer PER 160196
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 142613
gaspar.iii.coligny PER 7877
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 210499
john.vere PER 94659
antonio.lando PER 267755
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 107069
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 9162
michiel.pagani PER 94366
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 179208
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 258933
hans.meinhard PER 75039
...
Each line corresponds to a marked entity occurrence. Lines consist of tab separated fields:
- entity identifier
- entity kind
- remaining fields: slots, i.e. the textual positions occupied by the occurrence. Some entity occurrences consist of multiple words / tokens, hence have multiple slots.
Expand source code Browse git
"""API for rule-based entity marking.
This module contains the top-level methods for applying annotation rules to a corpus.
To see how this fits among all the modules of this package, see
`tf.browser.ner.annotate` .
# Programmatic annotation done in a Jupyter Notebook
If you have a spreadsheet with named entities, and for each entity a list of surface forms,
then this module takes care to read that spreadsheet, translate it to YAML,
and then use the YAML as instructions to add entity annotations to the corpus.
See this
[example notebook](https://nbviewer.jupyter.org/github/HuygensING/suriano/blob/main/programs/ner.ipynb).
Here are more details.
## Starting up
Load the relevant Python modules:
``` python
from tf.app import use
```
Load your corpus. There are two ways:
* Work with a local GitHub clone of the corpus in `~/HuygensING/suriano`:
A = use("HuygensING/suriano:clone", checkout="clone")
* Or let TF auto-download the latest version and work with that:
A = use("HuygensING/suriano")
Load the `Ner` module:
``` python
NE = A.makeNer()
```
The tool expects some input data to be present: configuration and spreadsheets with
instructions. They can be found in the `ner` directory.
If you work with a local GitHub clone, that data resides in
`~/github/HuygensING/suriano`
and if you work with an auto-downloaded copy of the data, it is in
`~/text-fabric-data/github/HuygensING/suriano`.
The output data of the tool ends up in the `_temp` directory, which ends up next
to the `ner` directory.
## The entity spreadsheets
Here is an example:

In our example, the name of the spreadsheet containing this information is
`people.xlsx` and it can be found as `ner/sheets/people.xlsx`
The spreadsheet will be read as follows:
* the first two rows will be skipped
* after that, each row is taken to describe exactly one entity
* the first column has the full and unique name for that entity
* the second column contains the kind of the entity (you may choose your
keywords freely for this)
* the third column contains a number of surface forms for this entity,
separated by `;`
* when the surface forms are peeled out, leading and trailing white-space will be
stripped
* all other columns will be ignored for the moment; in later versions we may use
the information in those columns to fill in extra data about the entities;
but probably that information will not end up in TF features.
During translation from XLSX to YAML the following happens:
* An identifier is distilled from the name of the entity;
* Missing kind fields are filled with the default kind.
These steps need some configuration information from the `ner/config.yaml` file.
Translation is done by
``` python
NE.readInstructions("people")
```
The resulting YAML ends up next to the
spreadsheet, and it looks like this:
``` yaml
christoffel.sticke:
kind: PER
name: Christoffel Sticke
occSpecs: []
diederik.sticke:
kind: PER
name: Diederik Sticke
occSpecs:
- Dierck
- Dirk
dirck.hartog:
kind: PER
name: Dirck Hartog
occSpecs:
- Dirich Hartocson
- Hertocson
jan.baptist.roelants:
kind: PER
name: Jan-Baptist Roelants
occSpecs:
- Roelans
- Rolans
```
## Inventory
A first step is to find out how many occurrences we find in the corpus for these
surface forms:
``` python
NE.makeInventory()
NE.showInventory()
```
and the output looks like this
```
...
cornelis.adriaensz PER Pach 7 x Cornelis Adriaensz. Pack
david.marlot PER Morlot 1 x David de Marlot
erick.dimmer PER Dimer 11 x Erick Dimmer
erycius.puteanus PER Potiano 2 x Erycius Puteanus
francesco.giustiniani PER Giustiniano 11 x Francesco Giustiniani
francois.doubleth PER Doublet 2 x François Doubleth
...
Total 150
```
Entities that are in the spreadsheet, but not in the corpus are skipped.
## Marking up
In order to create annotations for these entities, we have to switch to an
annotation set. Let's start a new set and give it the name `power`.
``` python
NE.setSet("power")
```
If it turns out that `power` has already annotations, and you want to clear them, say
``` python
NE.resetSet("power")
```
Now we are ready for the big thing: creating the annotations:
``` python
NE.markEntities()
```
It outputs this message:
```
Already present: 0 x
Added: 150 x
```
## Inspection
We now revert to lower-level methods from the `tf.browser.ner.annotate` class to
inspect some of the results.
``` python
results = NE.filterContent(bFind="pach", bFindC=False, anyEnt=True, showStats=None)
```
Here we filtered the chunks (paragraphs) to those that contain the string `pach`,
in a case-insensitive way, and that contain at least one entity.
There 6 of them, and we can show them:
``` python
NE.showContent(results)
```

The resulting entities are in `_temp/power/entities.tsv` and look like this:
```
erick.dimmer PER 160196
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 142613
gaspar.iii.coligny PER 7877
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 210499
john.vere PER 94659
antonio.lando PER 267755
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 107069
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 9162
michiel.pagani PER 94366
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 179208
isabella.clara.eugenia PER 258933
hans.meinhard PER 75039
...
```
Each line corresponds to a marked entity occurrence.
Lines consist of tab separated fields:
* entity identifier
* entity kind
* remaining fields: slots, i.e. the textual positions occupied by the occurrence.
Some entity occurrences consist of multiple words / tokens, hence have multiple
slots.
"""
from ...capable import CheckImport
from ...core.files import mTime, fileExists, readYaml, writeYaml
from ...core.helpers import console
from .helpers import normalize, toSmallId, toTokens
from .annotate import Annotate
class NER(Annotate):
def __init__(self, app):
"""Bulk entity annotation.
Contains methods to translate spreadsheets to YAML files with markup
instructions; to locate all relevant occurrences; and to mark them up
properly.
It is a high-level class, building on the lower-level tools provided
by the Annotate class on which it is based.
Parameters
----------
app: object
The object that corresponds to a loaded TF app for a corpus.
"""
super().__init__(app)
if not self.properlySetup:
return
self.instructions = None
"""Will contain the information in a spreadsheet for marking up entities."""
self.inventory = None
"""Will contain the locations of all surface forms in the current instructions.
"""
def readInstructions(self, sheetName, force=False):
"""Reads an Excel or YAML file with entity recognition instructions.
If an Excel spreadsheet is present and no corresponding YAML file is present,
or if the corresponding YAML file is out of data, the spreadsheet will be
converted to YAML.
The info in the resulting YAML file is stored as attribute
`instructions` in this object.
A report of the instructions will be shown in the output.
Reading instructions will invalidate the `inventory` member of this object,
which is the result of looking up all entities in the corpus on the basis
of the instructions.
Parameters
----------
sheetName: string
The file name without extension of the spreadsheet.
The spreadsheet is expected in the `ner/sheets` directory.
The YAML file ends up in the same directory, with the same name and
extension `.yaml`
force: boolean, optional False
If True, the conversion from Excel to YAML will take place anyhow, provided
the Excel sheet exists.
"""
CI = CheckImport("openpyxl")
if CI.importOK(hint=True):
openpyxl = CI.importGet()
load_workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook
else:
return
if not self.properlySetup:
return
sheetDir = self.sheetDir
xlsFile = f"{sheetDir}/{sheetName}.xlsx"
yamlFile = f"{sheetDir}/{sheetName}.yaml"
doConvert = False
if not fileExists(yamlFile):
if not fileExists(xlsFile):
console(f"no instructions found: {yamlFile} and {xlsFile} don't exist")
return
doConvert = True
else:
if fileExists(xlsFile) and force or (mTime(yamlFile) < mTime(xlsFile)):
doConvert = True
if doConvert:
settings = self.settings
transform = settings.transform
keywordFeatures = settings.keywordFeatures
kindFeature = keywordFeatures[0]
defaultValues = settings.defaultValues
wb = load_workbook(xlsFile, data_only=True)
ws = wb.active
(headRow, subHeadRow, *rows) = list(ws.rows)
rows = [row for row in rows if any(c.value for c in row)]
defaultKind = defaultValues.get(kindFeature, "")
info = {}
namesByOrigEid = {}
eidByName = {}
for r, row in enumerate(ws.rows):
if r in {0, 1}:
continue
if not any(c.value for c in row):
continue
(name, kind, synonymStr) = (
normalize(row[i].value or "") for i in range(3)
)
synonyms = sorted(
set()
if not synonymStr
else {normalize(x) for x in synonymStr.split(";")}
)
if not name:
name = synonyms[0] if synonyms else ""
if name == "":
console(f"Row {r + 1:>3}: no entity name and no synonyms")
continue
else:
console(f"Row {r + 1:>3}: no entity name, supplied {name}")
if not kind:
kind = defaultKind
i = 0
while name in eidByName:
i += 1
name = f"{name} ({i})"
eid = toSmallId(name, transform=transform)
namesByOrigEid.setdefault(eid, []).append(name)
i = 0
while eid in info:
i += 1
eid = f"{eid}.{i}"
eidByName[name] = eid
occSpecs = sorted(synonyms, key=lambda x: -len(x))
info[eid] = {"name": name, kindFeature: kind, "occSpecs": occSpecs}
for origEid, names in sorted(namesByOrigEid.items()):
if len(names) == 1:
continue
console(f"Multiple names for candidate identifier {origEid}:")
for name in names:
newEid = eidByName[name]
console(f"""\tIdentifier {newEid} assigned to name "{name}" """)
writeYaml(info, asFile=yamlFile)
else:
info = readYaml(asFile=yamlFile)
namesByOcc = {}
for eInfo in info.values():
name = eInfo["name"]
occSpecs = eInfo["occSpecs"]
for occSpec in occSpecs:
namesByOcc.setdefault(occSpec, []).append(name)
nEid = len(info)
nOcc = sum(len(x["occSpecs"]) for x in info.values())
noOccs = sum(1 for x in info.values() if len(x["occSpecs"]) == 0)
console(f"{nEid} entities with {nOcc} occurrence specs")
console(f"{noOccs} entities do not have occurrence specifiers")
nm = 0
for occSpec, names in sorted(namesByOcc.items()):
if len(names) == 1:
continue
console(f""""{occSpec}" used for:""")
for name in names:
console(f"\t{name}")
nm += 1
if nm == 0:
console("All occurrence specifiers are unambiguous")
else:
console(f"{nm} occurrence specifiers are ambiguous")
self.instructions = readYaml(asFile=yamlFile)
self.inventory = None
def makeInventory(self):
"""Explores the corpus for the surface forms mentioned in the instructions.
The instructions are present in the `instructions` attribute of the object.
The resulting inventory is stored in the `inventory` member of
the object.
It is a dictionary, keyed by sequences of tokens, whose values are the
slot sequences where those token sequences occur in the corpus.
"""
if not self.properlySetup:
return
instructions = self.instructions
settings = self.settings
spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped
qSets = set()
for info in instructions.values():
for occSpec in info.occSpecs:
qSets.add(toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped))
self.inventory = self.findOccs(qSets)
def showInventory(self):
"""Shows the inventory.
The surface forms in the inventory are put into the context of the entities
of which they are surface forms.
"""
if not self.properlySetup:
return
instructions = self.instructions
inventory = self.inventory
settings = self.settings
spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped
total = 0
for eid, info in instructions.items():
name = info.name
kind = info.kind
occSpecs = info.occSpecs
for occSpec in occSpecs:
matches = inventory.get(toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped), None)
if matches is None:
continue
n = len(matches)
total += n
console(f"{eid:<24} {kind:<5} {occSpec:<20} {n:>5} x {name}")
console(f"Total {total}")
def markEntities(self):
"""Marks up the members of the inventory as entities.
The instructions contain the entity identifier and the entity kind that
have to be assigned to the surface forms.
The inventory knows where the occurrences of the surface forms are.
If there is no inventory yet, it will be created.
"""
if not self.properlySetup:
return
inventory = self.inventory
instructions = self.instructions
settings = self.settings
spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped
keywordFeatures = settings.keywordFeatures
kindFeature = keywordFeatures[0]
newEntities = []
qSets = set()
fValsByQTokens = {}
for eid, info in instructions.items():
kind = info[kindFeature]
occSpecs = info.occSpecs
if not len(occSpecs):
continue
for occSpec in info.occSpecs:
qTokens = toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped)
fValsByQTokens.setdefault(qTokens, set()).add((eid, kind))
qSets.add(qTokens)
if inventory is None:
inventory = self.findOccs(qSets)
self.inventory = inventory
for qTokens, matches in inventory.items():
for fVals in fValsByQTokens[qTokens]:
newEntities.append((fVals, matches))
self.addEntities(newEntities, silent=False)Classes
class NER (app)-
Bulk entity annotation.
Contains methods to translate spreadsheets to YAML files with markup instructions; to locate all relevant occurrences; and to mark them up properly.
It is a high-level class, building on the lower-level tools provided by the Annotate class on which it is based.
Parameters
app:object- The object that corresponds to a loaded TF app for a corpus.
Expand source code Browse git
class NER(Annotate): def __init__(self, app): """Bulk entity annotation. Contains methods to translate spreadsheets to YAML files with markup instructions; to locate all relevant occurrences; and to mark them up properly. It is a high-level class, building on the lower-level tools provided by the Annotate class on which it is based. Parameters ---------- app: object The object that corresponds to a loaded TF app for a corpus. """ super().__init__(app) if not self.properlySetup: return self.instructions = None """Will contain the information in a spreadsheet for marking up entities.""" self.inventory = None """Will contain the locations of all surface forms in the current instructions. """ def readInstructions(self, sheetName, force=False): """Reads an Excel or YAML file with entity recognition instructions. If an Excel spreadsheet is present and no corresponding YAML file is present, or if the corresponding YAML file is out of data, the spreadsheet will be converted to YAML. The info in the resulting YAML file is stored as attribute `instructions` in this object. A report of the instructions will be shown in the output. Reading instructions will invalidate the `inventory` member of this object, which is the result of looking up all entities in the corpus on the basis of the instructions. Parameters ---------- sheetName: string The file name without extension of the spreadsheet. The spreadsheet is expected in the `ner/sheets` directory. The YAML file ends up in the same directory, with the same name and extension `.yaml` force: boolean, optional False If True, the conversion from Excel to YAML will take place anyhow, provided the Excel sheet exists. """ CI = CheckImport("openpyxl") if CI.importOK(hint=True): openpyxl = CI.importGet() load_workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook else: return if not self.properlySetup: return sheetDir = self.sheetDir xlsFile = f"{sheetDir}/{sheetName}.xlsx" yamlFile = f"{sheetDir}/{sheetName}.yaml" doConvert = False if not fileExists(yamlFile): if not fileExists(xlsFile): console(f"no instructions found: {yamlFile} and {xlsFile} don't exist") return doConvert = True else: if fileExists(xlsFile) and force or (mTime(yamlFile) < mTime(xlsFile)): doConvert = True if doConvert: settings = self.settings transform = settings.transform keywordFeatures = settings.keywordFeatures kindFeature = keywordFeatures[0] defaultValues = settings.defaultValues wb = load_workbook(xlsFile, data_only=True) ws = wb.active (headRow, subHeadRow, *rows) = list(ws.rows) rows = [row for row in rows if any(c.value for c in row)] defaultKind = defaultValues.get(kindFeature, "") info = {} namesByOrigEid = {} eidByName = {} for r, row in enumerate(ws.rows): if r in {0, 1}: continue if not any(c.value for c in row): continue (name, kind, synonymStr) = ( normalize(row[i].value or "") for i in range(3) ) synonyms = sorted( set() if not synonymStr else {normalize(x) for x in synonymStr.split(";")} ) if not name: name = synonyms[0] if synonyms else "" if name == "": console(f"Row {r + 1:>3}: no entity name and no synonyms") continue else: console(f"Row {r + 1:>3}: no entity name, supplied {name}") if not kind: kind = defaultKind i = 0 while name in eidByName: i += 1 name = f"{name} ({i})" eid = toSmallId(name, transform=transform) namesByOrigEid.setdefault(eid, []).append(name) i = 0 while eid in info: i += 1 eid = f"{eid}.{i}" eidByName[name] = eid occSpecs = sorted(synonyms, key=lambda x: -len(x)) info[eid] = {"name": name, kindFeature: kind, "occSpecs": occSpecs} for origEid, names in sorted(namesByOrigEid.items()): if len(names) == 1: continue console(f"Multiple names for candidate identifier {origEid}:") for name in names: newEid = eidByName[name] console(f"""\tIdentifier {newEid} assigned to name "{name}" """) writeYaml(info, asFile=yamlFile) else: info = readYaml(asFile=yamlFile) namesByOcc = {} for eInfo in info.values(): name = eInfo["name"] occSpecs = eInfo["occSpecs"] for occSpec in occSpecs: namesByOcc.setdefault(occSpec, []).append(name) nEid = len(info) nOcc = sum(len(x["occSpecs"]) for x in info.values()) noOccs = sum(1 for x in info.values() if len(x["occSpecs"]) == 0) console(f"{nEid} entities with {nOcc} occurrence specs") console(f"{noOccs} entities do not have occurrence specifiers") nm = 0 for occSpec, names in sorted(namesByOcc.items()): if len(names) == 1: continue console(f""""{occSpec}" used for:""") for name in names: console(f"\t{name}") nm += 1 if nm == 0: console("All occurrence specifiers are unambiguous") else: console(f"{nm} occurrence specifiers are ambiguous") self.instructions = readYaml(asFile=yamlFile) self.inventory = None def makeInventory(self): """Explores the corpus for the surface forms mentioned in the instructions. The instructions are present in the `instructions` attribute of the object. The resulting inventory is stored in the `inventory` member of the object. It is a dictionary, keyed by sequences of tokens, whose values are the slot sequences where those token sequences occur in the corpus. """ if not self.properlySetup: return instructions = self.instructions settings = self.settings spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped qSets = set() for info in instructions.values(): for occSpec in info.occSpecs: qSets.add(toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped)) self.inventory = self.findOccs(qSets) def showInventory(self): """Shows the inventory. The surface forms in the inventory are put into the context of the entities of which they are surface forms. """ if not self.properlySetup: return instructions = self.instructions inventory = self.inventory settings = self.settings spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped total = 0 for eid, info in instructions.items(): name = info.name kind = info.kind occSpecs = info.occSpecs for occSpec in occSpecs: matches = inventory.get(toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped), None) if matches is None: continue n = len(matches) total += n console(f"{eid:<24} {kind:<5} {occSpec:<20} {n:>5} x {name}") console(f"Total {total}") def markEntities(self): """Marks up the members of the inventory as entities. The instructions contain the entity identifier and the entity kind that have to be assigned to the surface forms. The inventory knows where the occurrences of the surface forms are. If there is no inventory yet, it will be created. """ if not self.properlySetup: return inventory = self.inventory instructions = self.instructions settings = self.settings spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped keywordFeatures = settings.keywordFeatures kindFeature = keywordFeatures[0] newEntities = [] qSets = set() fValsByQTokens = {} for eid, info in instructions.items(): kind = info[kindFeature] occSpecs = info.occSpecs if not len(occSpecs): continue for occSpec in info.occSpecs: qTokens = toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped) fValsByQTokens.setdefault(qTokens, set()).add((eid, kind)) qSets.add(qTokens) if inventory is None: inventory = self.findOccs(qSets) self.inventory = inventory for qTokens, matches in inventory.items(): for fVals in fValsByQTokens[qTokens]: newEntities.append((fVals, matches)) self.addEntities(newEntities, silent=False)Ancestors
Instance variables
var instructions-
Will contain the information in a spreadsheet for marking up entities.
var inventory-
Will contain the locations of all surface forms in the current instructions.
Methods
def makeInventory(self)-
Explores the corpus for the surface forms mentioned in the instructions.
The instructions are present in the
instructionsattribute of the object.The resulting inventory is stored in the
inventorymember of the object.It is a dictionary, keyed by sequences of tokens, whose values are the slot sequences where those token sequences occur in the corpus.
Expand source code Browse git
def makeInventory(self): """Explores the corpus for the surface forms mentioned in the instructions. The instructions are present in the `instructions` attribute of the object. The resulting inventory is stored in the `inventory` member of the object. It is a dictionary, keyed by sequences of tokens, whose values are the slot sequences where those token sequences occur in the corpus. """ if not self.properlySetup: return instructions = self.instructions settings = self.settings spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped qSets = set() for info in instructions.values(): for occSpec in info.occSpecs: qSets.add(toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped)) self.inventory = self.findOccs(qSets) def markEntities(self)-
Marks up the members of the inventory as entities.
The instructions contain the entity identifier and the entity kind that have to be assigned to the surface forms.
The inventory knows where the occurrences of the surface forms are. If there is no inventory yet, it will be created.
Expand source code Browse git
def markEntities(self): """Marks up the members of the inventory as entities. The instructions contain the entity identifier and the entity kind that have to be assigned to the surface forms. The inventory knows where the occurrences of the surface forms are. If there is no inventory yet, it will be created. """ if not self.properlySetup: return inventory = self.inventory instructions = self.instructions settings = self.settings spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped keywordFeatures = settings.keywordFeatures kindFeature = keywordFeatures[0] newEntities = [] qSets = set() fValsByQTokens = {} for eid, info in instructions.items(): kind = info[kindFeature] occSpecs = info.occSpecs if not len(occSpecs): continue for occSpec in info.occSpecs: qTokens = toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped) fValsByQTokens.setdefault(qTokens, set()).add((eid, kind)) qSets.add(qTokens) if inventory is None: inventory = self.findOccs(qSets) self.inventory = inventory for qTokens, matches in inventory.items(): for fVals in fValsByQTokens[qTokens]: newEntities.append((fVals, matches)) self.addEntities(newEntities, silent=False) def readInstructions(self, sheetName, force=False)-
Reads an Excel or YAML file with entity recognition instructions.
If an Excel spreadsheet is present and no corresponding YAML file is present, or if the corresponding YAML file is out of data, the spreadsheet will be converted to YAML.
The info in the resulting YAML file is stored as attribute
instructionsin this object.A report of the instructions will be shown in the output.
Reading instructions will invalidate the
inventorymember of this object, which is the result of looking up all entities in the corpus on the basis of the instructions.Parameters
sheetName:string- The file name without extension of the spreadsheet.
The spreadsheet is expected in the
ner/sheetsdirectory. The YAML file ends up in the same directory, with the same name and extension.yaml force:boolean, optionalFalse- If True, the conversion from Excel to YAML will take place anyhow, provided the Excel sheet exists.
Expand source code Browse git
def readInstructions(self, sheetName, force=False): """Reads an Excel or YAML file with entity recognition instructions. If an Excel spreadsheet is present and no corresponding YAML file is present, or if the corresponding YAML file is out of data, the spreadsheet will be converted to YAML. The info in the resulting YAML file is stored as attribute `instructions` in this object. A report of the instructions will be shown in the output. Reading instructions will invalidate the `inventory` member of this object, which is the result of looking up all entities in the corpus on the basis of the instructions. Parameters ---------- sheetName: string The file name without extension of the spreadsheet. The spreadsheet is expected in the `ner/sheets` directory. The YAML file ends up in the same directory, with the same name and extension `.yaml` force: boolean, optional False If True, the conversion from Excel to YAML will take place anyhow, provided the Excel sheet exists. """ CI = CheckImport("openpyxl") if CI.importOK(hint=True): openpyxl = CI.importGet() load_workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook else: return if not self.properlySetup: return sheetDir = self.sheetDir xlsFile = f"{sheetDir}/{sheetName}.xlsx" yamlFile = f"{sheetDir}/{sheetName}.yaml" doConvert = False if not fileExists(yamlFile): if not fileExists(xlsFile): console(f"no instructions found: {yamlFile} and {xlsFile} don't exist") return doConvert = True else: if fileExists(xlsFile) and force or (mTime(yamlFile) < mTime(xlsFile)): doConvert = True if doConvert: settings = self.settings transform = settings.transform keywordFeatures = settings.keywordFeatures kindFeature = keywordFeatures[0] defaultValues = settings.defaultValues wb = load_workbook(xlsFile, data_only=True) ws = wb.active (headRow, subHeadRow, *rows) = list(ws.rows) rows = [row for row in rows if any(c.value for c in row)] defaultKind = defaultValues.get(kindFeature, "") info = {} namesByOrigEid = {} eidByName = {} for r, row in enumerate(ws.rows): if r in {0, 1}: continue if not any(c.value for c in row): continue (name, kind, synonymStr) = ( normalize(row[i].value or "") for i in range(3) ) synonyms = sorted( set() if not synonymStr else {normalize(x) for x in synonymStr.split(";")} ) if not name: name = synonyms[0] if synonyms else "" if name == "": console(f"Row {r + 1:>3}: no entity name and no synonyms") continue else: console(f"Row {r + 1:>3}: no entity name, supplied {name}") if not kind: kind = defaultKind i = 0 while name in eidByName: i += 1 name = f"{name} ({i})" eid = toSmallId(name, transform=transform) namesByOrigEid.setdefault(eid, []).append(name) i = 0 while eid in info: i += 1 eid = f"{eid}.{i}" eidByName[name] = eid occSpecs = sorted(synonyms, key=lambda x: -len(x)) info[eid] = {"name": name, kindFeature: kind, "occSpecs": occSpecs} for origEid, names in sorted(namesByOrigEid.items()): if len(names) == 1: continue console(f"Multiple names for candidate identifier {origEid}:") for name in names: newEid = eidByName[name] console(f"""\tIdentifier {newEid} assigned to name "{name}" """) writeYaml(info, asFile=yamlFile) else: info = readYaml(asFile=yamlFile) namesByOcc = {} for eInfo in info.values(): name = eInfo["name"] occSpecs = eInfo["occSpecs"] for occSpec in occSpecs: namesByOcc.setdefault(occSpec, []).append(name) nEid = len(info) nOcc = sum(len(x["occSpecs"]) for x in info.values()) noOccs = sum(1 for x in info.values() if len(x["occSpecs"]) == 0) console(f"{nEid} entities with {nOcc} occurrence specs") console(f"{noOccs} entities do not have occurrence specifiers") nm = 0 for occSpec, names in sorted(namesByOcc.items()): if len(names) == 1: continue console(f""""{occSpec}" used for:""") for name in names: console(f"\t{name}") nm += 1 if nm == 0: console("All occurrence specifiers are unambiguous") else: console(f"{nm} occurrence specifiers are ambiguous") self.instructions = readYaml(asFile=yamlFile) self.inventory = None def showInventory(self)-
Shows the inventory.
The surface forms in the inventory are put into the context of the entities of which they are surface forms.
Expand source code Browse git
def showInventory(self): """Shows the inventory. The surface forms in the inventory are put into the context of the entities of which they are surface forms. """ if not self.properlySetup: return instructions = self.instructions inventory = self.inventory settings = self.settings spaceEscaped = settings.spaceEscaped total = 0 for eid, info in instructions.items(): name = info.name kind = info.kind occSpecs = info.occSpecs for occSpec in occSpecs: matches = inventory.get(toTokens(occSpec, spaceEscaped=spaceEscaped), None) if matches is None: continue n = len(matches) total += n console(f"{eid:<24} {kind:<5} {occSpec:<20} {n:>5} x {name}") console(f"Total {total}")
Inherited members
Annotate:addEntitiesaddEntityaddEntityRichannoSetannoSetRepcheckBucketscheckFeatureconsoledelEntitydelEntityRichfeatureDefaultfilterContentfindOccsfromSourceget0get1getAftergetBucketNodesgetContextgetEntityNodesgetFValgetSetDatagetSlotsgetStrgetStringsgetTextgetTextRgetTokensloadDatamergeEntitiesprocessproperlySetupresetSetsaveEntitiesAssectionHeadsetDelsetDupsetMovesetNamessetSetshowContentshowEntitiesshowEntityOverviewslotTypeweedEntities